Human IL-18 ELISA Kit检测试剂盒(酶联免疫吸附法)
¥1,600.00 – ¥2,650.00
因产品会迭代升级,具体实验步骤请按纸质版说明书操作
在售SKU:70-EK118-48, 70-EK118-96, EK118
- 分子靶点:IL18
- 种属:人
- 样本类型:血清、血浆、细胞培养上清
- 检测样本体积:血清血浆:20μL;细胞培养上清:100μL
- 灵敏度:19.52pg/mL
- 检测范围:0.16-10ng/mL
- 回收率:87%-114%
ELISA试剂盒详细信息
| 商品名 | 人 IL-18 酶联免疫检测试剂盒 |
|---|---|
| 种属 | 人 |
| 靶点 | IL18 |
| 检测方法 | 双抗体夹心法 |
| 检测样本类型 | 血清、血浆、细胞培养上清 |
| 检测样本体积 | 血清血浆:20μL;细胞培养上清:100μL |
| 灵敏度 | 19.52pg/mL |
| 线性范围 | 0.16-10ng/mL |
| 精密度 | 板内变异系数:3.4%-6.4%;板间变异系数:3.4%-4.7% |
| 回收率 | 87%-114% |
| 平均回收率 | 100% |
| 板式 | 96孔板,可拆 |
| 保存条件 | 2-8℃保存。已拆开:标准品-20℃保存,其它4℃。 |
| 运输条件 | 2-8℃冰袋运输 |
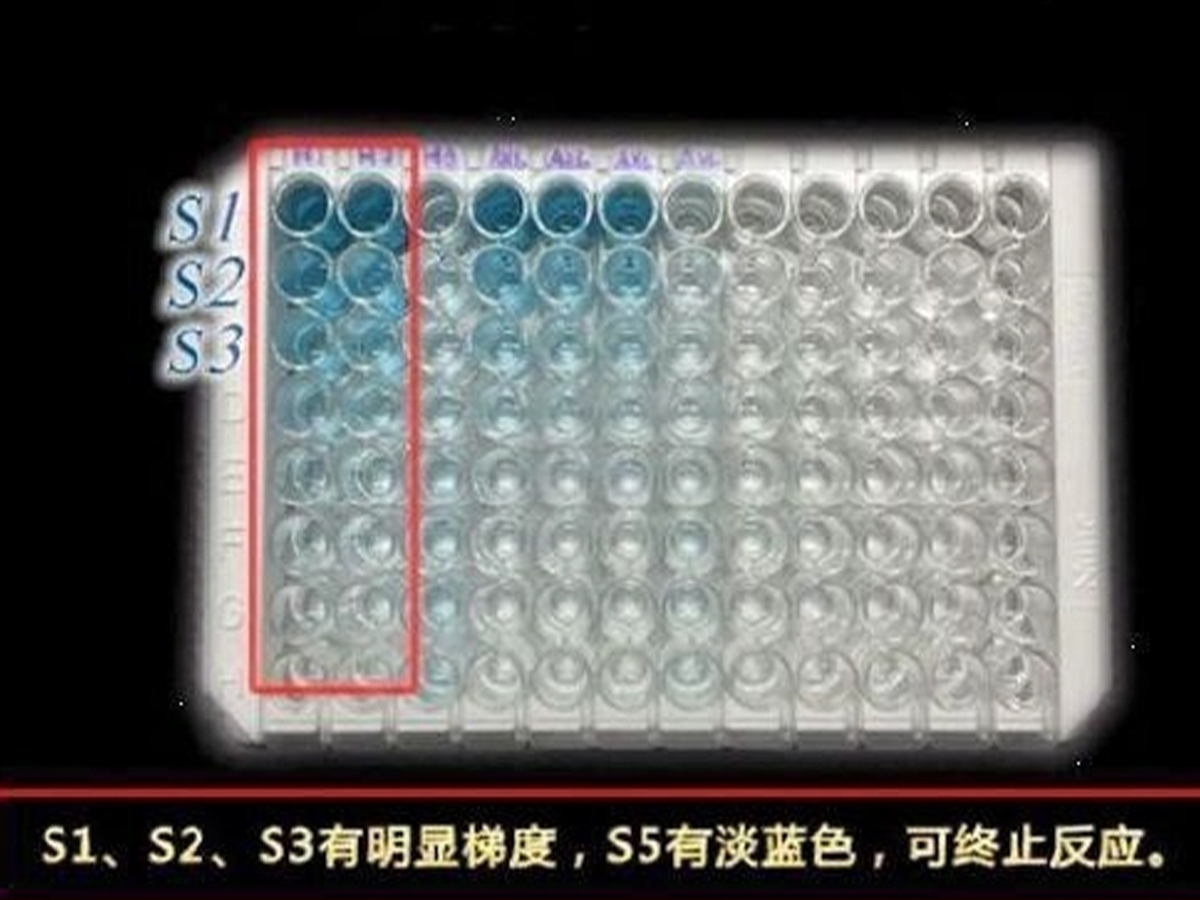
| 检测原理 | 本试剂盒采用双抗体夹心酶联免疫吸附检测技术。特异性抗人IL-18抗体预包被在高亲和力的酶标板上。酶标板孔中加入标准品、待测样本和辣根过氧化物酶标记检测抗体,经过孵育,样本中存在的IL-18与固相抗体和检测抗体结合。洗涤去除未结合的物质后,加入显色底物TMB,避光显色。颜色反应的深浅与样本中IL-18的浓度成正比。加入终止液终止反应,在450nm波长(参考波长570 - 630nm)测定吸光度值。 |
分子信息
IL18 分子靶点信息概述
- 分子名:IL18, interleukin 18
- 基因家族:Interleukins
- 别名:IGIF; IL1F4; IL-1g; IL-18
- 全称:interferon-gamma-inducing factor; interleukin 18 (interferon-gamma-inducing factor)
IL18 分子靶点综述
白细胞介素18(IL-18),又名干扰素γ诱导因子,是一种促炎性细胞因子,在人类中由IL18基因编码。IL-18属于IL-1超家族,由巨噬细胞和其它细胞分泌产生。IL-18刺激后,自然杀伤细胞(NK)和某些T细胞就会释放另一种重要的细胞因子—干扰素γ或Ⅱ型干扰素,进而激活巨噬细胞或其它细胞。IL-18可诱导产生严重的炎症反应,同样可增加人类神经元中β-淀粉样蛋白(与阿尔茨海默氏病相关)的产生。
人 Human IL18 分子靶点信息
- 分子名:IL18, interleukin 18
- 别称:
- iboctadekin
- IFN-gamma-inducing factor
- IGIF
- IL-1 gamma
- IL-18
- IL-1g
- IL1F4
- interferon gamma-inducing factor
- interleukin 18 (interferon-gamma-inducing factor)
- interleukin-1 gamma
- interleukin-18
- MGC12320
- 基因序列:NCBI_Gene: 3606
- 蛋白序列:UniProtKB: Q14116
人 Human IL18靶点分子功能(预测)
Enables cytokine activity and interleukin-18 receptor binding activity. Involved in several processes, including positive regulation of cell population proliferation; positive regulation of intracellular signal transduction; and positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process. Located in extracellular space. Implicated in several diseases, including Kawasaki disease; allergic rhinitis; autoimmune disease (multiple); biliary atresia; and hepatitis B. Biomarker of several diseases, including autoimmune disease (multiple); cholestasis (multiple); liver disease (multiple); lung disease (multiple); and myositis (multiple).