|
细胞表面的PS外翻在1995年首次报道为细胞凋亡的显著特征,并被大量实验引用,长期以来,PS的外翻被认为是细胞凋亡中不可逆的行为,然而近年来文献报道PS的外翻是可逆的,不仅存在于凋亡细胞中,也存在于其他细胞形态中。pSIVA-IANBD技术的出现可以实时追踪PS的外翻,使科研工作者获得更多不同类型细胞死亡中的细胞膜极性变化信息。
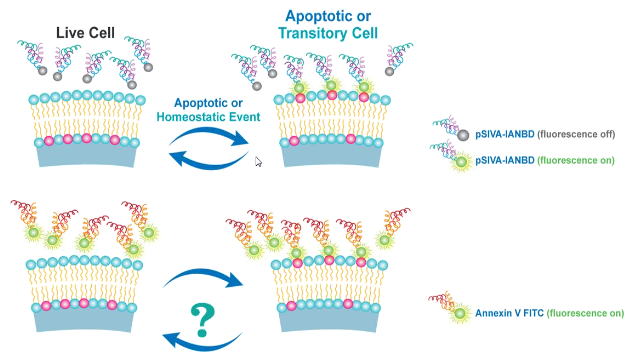
pSIVA(Polarity Sensitive Indicator of Viability & Apoptosis)凋亡检测技术是Novus 2010年推出的一项新型技术,并于2013年发布专利。该技术使用的pSIVA是一种Ca2+依赖性蛋白,与磷酯酰丝氨酸(PS)有非常高的结合能力,其与IANBD极性染料偶联后形成pSIVA-IANBD复合物,这种复合物只有结合PS才会产生荧光。如下图所示:
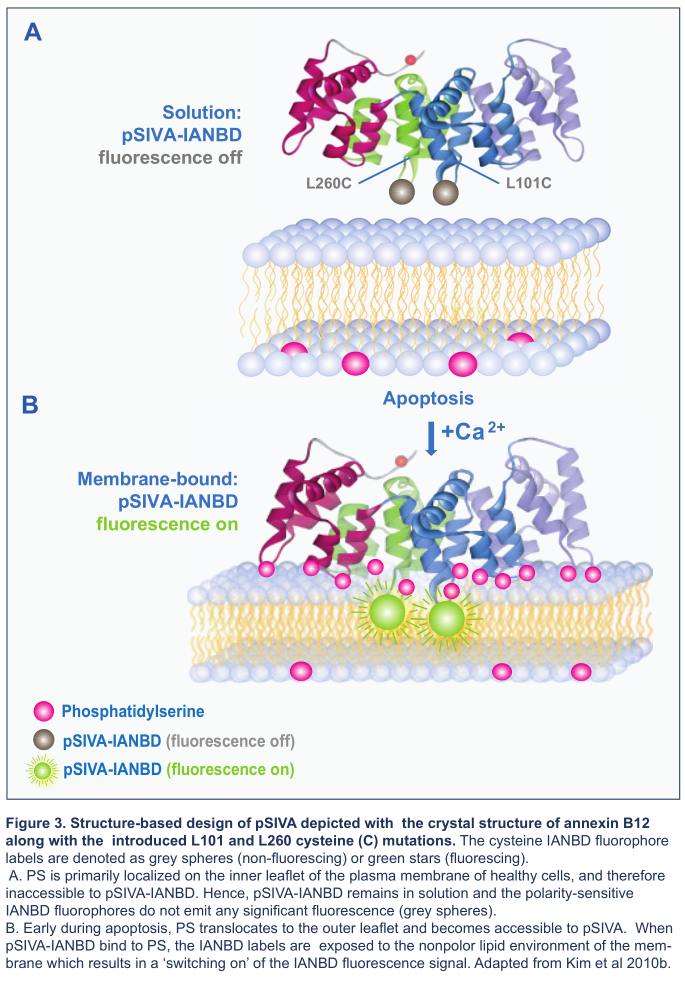
而传统的Annexin V检测技术,无论是否与PS结合,荧光始终存在,无法区分PS的瞬时与不可逆外翻,因此,相比较Annexin V,pSIVA能够做到让细胞凋亡检测更精准。
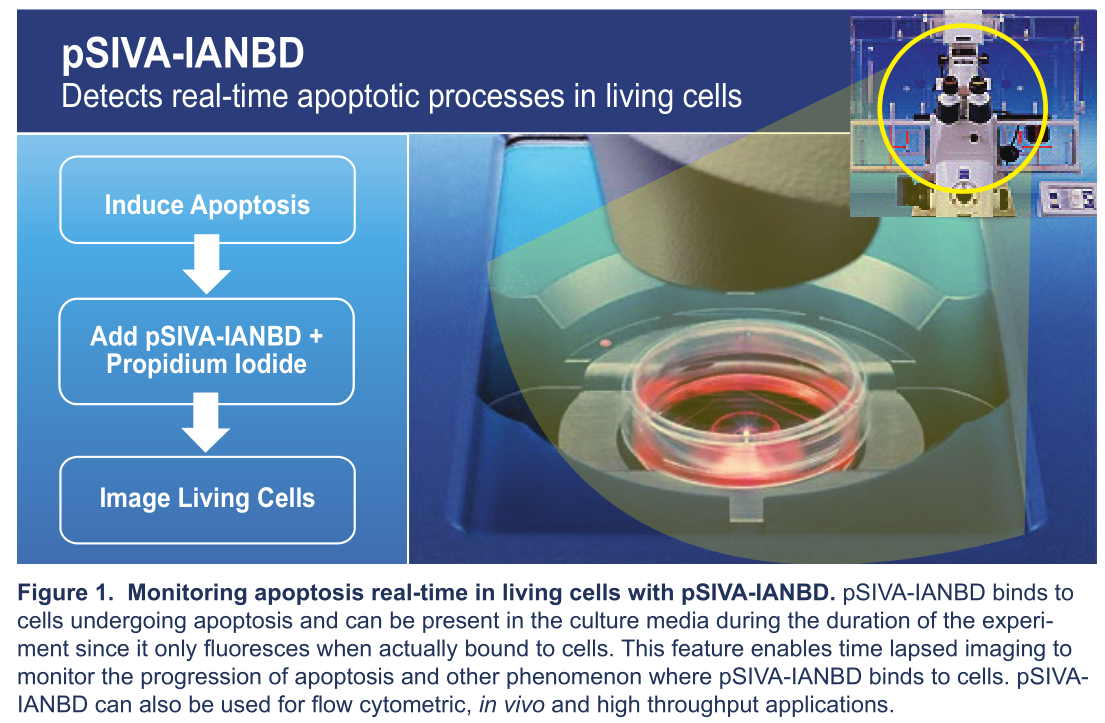
| Novus pSIVA试剂盒让凋亡检测更快更精准更直观!Novus pSIVA凋亡检测试剂盒自上市以来,受到广大科研工作者的喜爱与热捧,该试剂盒操作相当简单,只需将pSIVA-IANBD或pSIVA-IANBD+PI直接加入细胞或组织,孵育后便可检测,无需洗涤! |
 |
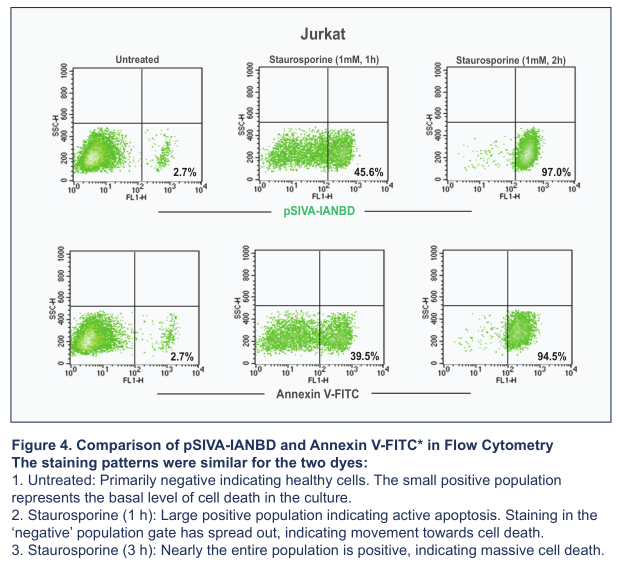
在流式应用方面,Novus pSIVA凋亡试剂盒与Annexin V相比有一样优异的表现:
在荧光观察方面,Novus pSIVA凋亡试剂盒比Annexin V表现更出色!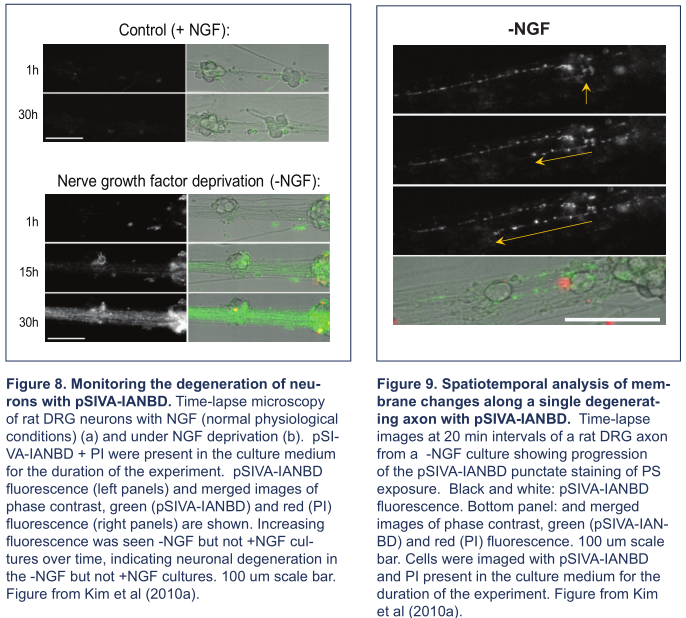
Novus pSIVA凋亡检测试剂盒产品列表
| 厂商 |
目录号 |
产品名称 |
规格 |
目录价 |
文献 |
| Novus |
H6-NBP2-29611-25Tests |
Polarity Sensitive Indicator ofViability Flow Assay Kit |
25Tests |
1850 |
13 |
| Novus |
H6-NBP2-29611-100Tests |
Polarity Sensitive Indicator ofViability Flow Assay Kit |
100Tests |
3040 |
13 |
| Novus |
H6-NBP2-29382-1SampleSizeKit |
Polarity Sensitive Indicator ofViability Apoptosis Microscopy Kit |
1 Sample Size Kit |
1770 |
22 |
| Novus |
H6-NBP2-29382 |
Polarity Sensitive Indicator ofViability Apoptosis Microscopy Kit |
1 Kit |
3040 |
22 |
Novus pSIVA—IANBD技术视频链接:
Novus pSIVA凋亡检测试剂盒部分引用文献列表:
[1]Neuronal deletion of caspase 8 protects against brain injury in mouse models of controlled cortical impact and kainic acid-induced excitotox- icity. Krajewska M, Z You, J Rong, C Kress, X Huang, J Yang, T Kyoda, R Leyva, S Banares, Y Hu, C-H Sze, MJ Whalen, L Salemena, R Hakem, BP Head, JC Reed, S Krajewski. PLOS ONE 6(9): e24341. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0024341 (2011). IF (mouse primary neuron cultures): Figs 2B, 3.Cells were labeled with pSIVA-IANBD for 15 min, fixed and stained with a MAP2 antibody and DAPI. Cells double-stained with both pSIVA-IANBD and MAP2 (neuronal marker) were identified as degenerating neurons.
[2] Hostile takeover by Plasmodium: reorganization of parasite and host cell membranes during liver stage egress. Graewe S, KE Rankin, C Lehmann, C Deschermeier, L Hecht, U Froehlke, RR Stanway, V Heussler. PLOS ONE 7(9): e1002224 doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1002224 (2011). IF (HepG2 cells infected with P. berghei parasites), Fig 1
[3] Mitochondrial NDUFS3 regulates the ROS-mediated onset of metabolic switch in transformed cells. Suhane S, H Kanzaki, V Arumugaswami, R Murali, VK Ramanujan. Biology Open doi: 10.1242/bio.20133244 (2013).pSIVA-IANBD Flow Kit: Flow (Cell Surface): Fig 1 (HEK293 cells). pSI- VA-IANBD was used to determine the basal level of apoptosis in HEK cells.
[4] Monitoring apoptosis and neuronal degeneration by real-time detection of phosphatidylserine externalization using a polarity-sensitive indica- tor of viability and apoptosis. Kim YE, J Chen, R Langen, JR Chan. Nature Protocols 5:1396-1405 (2010b). Time lapse microscopy of neurons innormal survival conditions and after NGF deprivation (Fig 2).
[5] A compact B model of huntingtin toxicity. Zhang CQ, Yeh T-l, A Leyva,LG Frank, J Miller, YE Kim, R Langen, S Finkbeiner, ML Amzel, CA Ross, MA Poirier. JBC 286:8188-8196 (2011). A pSIVA-IANBD based cell suspen- sion toxicity assay was used to determine cell viability in mouse Neu- ro2A (neuroblastoma) overexpressing huntingtin proteins (Fig 4).32 NBP2-29611 & NBP2-29382 pSIVA TM Kit pSIVA TM Kit Manual
[6] Diurnal, localized exposure of phosphatidylserine by rod outer seg-ment tips in wild-type but not Itgb5-/- or Mfge8-/- mouse retina. RuggieroL, MP Connor, J Chen, R Langen, SC Finnemann. PNAS 109:8145-4148(2012). Live tissue imaging (mouse retina): Figs 4, 5. S4. pSIVA-IANBDwas added to dissected live mouse retina and shown to label the tips of photoreceptor outer segments (POS).The results suggested that phosphatidylserine (PS) exposure is specif-ic to the POS surface. Furthermore, enhanced PS exposure preceded rod shedding and phagocytosis, suggesting that surface PS exposure promotes these processes.
[7]Characterization of cell cycle modifications induced by electric pulses in human corneal endothelium. Thi MH, Z He, N Campolmi, S Piselli, P Gain, M Peoc’H, JM Dumolllard, S Acquart, O Garraud, G Thuret. Acta Op- thalmologica 90:s249 (2012). Live tissue imaging (human cornea organ cultures): pSIVA-IANBD was used to assess cell death following gene electrotransfer into corneal endothelial cells.
[8.]Cell death goes LIVE: Technological advances in real-time tracking of cell death. Skommer J, Z Darzynkiewicz, D Wlodkowic. Cell Cycle 9:2330- 2341 (2010). Live cell imaging (etoposide treated cell lines & NGF-de-prived primary neuronal cultures): Discussion about tools for tracking cell death real-time.
[9]Annexin B12 Cys101,Cys260-N,N’-dimethyl-N-(iodoacetyl)-N’-(7-nitro-benz-2-oxa-1,3-diazol-4-yl)ethylenediamine. Shan L In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004-2013. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK45028/ (2010) Live cell imaging: The story of pSIVA as a phosphatidylserine-targeted, real-time, apoptosis-detecting probe.
[10] The change of cellular membranes on apoptosis: Fluorescence detection. Demchenko AP. Exp Oncol 34:263-268 (2012). Live imaging: Discussion about pSIVA as an important advancement in annexin based methodology.
[11]Real-time flow cytometry for the kinetic analysis of oncosis. Warnes G,S Martins. Cytometry Part A 79A:181-191 (2011). Live imaging: Discussion about pSIVA as an assay for real-time detection of apoptosis.
[12] Engineering a polarity-sensitive biosensor for time-lapse imaging of apoptotic processess and degeneration. Kim YE, J Chen, JR Chan, R Langen. Nature Methods 7:67-73 (2010a). Real-time live-cell imagingand time-lapse microscopy of apoptosis: Fig 2 (COS-7 cells), Fig 3 (rat33 NBP2-29611 & NBP2-29382 pSIVA TM KitpSIVA TM Kit Manual neuronal degeneration), Fig 4 (rat axonal degeneration), Fig 5 (rescue of rat neuronal degeneration as visualized by pSIVA.
[13]Monitoring apoptosis and neuronal degeneraton by real-time detection of posphatidylserine externalization using a polarity-sensitive indicator of viability and apoptosis. Kim YE, J Chen, R Langen, JR Chan. Nature Protocols 5:1396-1405 (2010b). Time lapse microscopy of neurons innormal survival conditions and after NGF deprivation (Fig 2).
[14] A compact beta model of huntingtin toxicity. Zhang CQ, Yeh T-I, A Leyva,LG Frank, J Miller, YE Kim, R Langen, S Finkbeiner, ML Amzel, CA Ross, MA Poirier. JBC 286:8188-8196 (2011). A pSIVA-IANBD based cell suspen- sion toxicity assay was used to determine cell viability in a mouse Neuro2A neuroblastoma cell line overexpressing huntingtin proteins (Fig 4).
[15]Hostile takeover by Plasmodium: reorganization of parasite and host cell membranes during liver stage egress. Graewe S, KE Rankin, CLehmann, C Deschermeier, L Hecht, U Froehike, RR Stanway, V Heussler. PLOS ONE 7(9): e1002224 doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1002224 (2011). IF (HepG2 cells infected with P. berghei parasites), Fig 1.
[16] Novel applications of pSIVA, a new polarity sensitive phosphatidylser-ine (PS) apoptosis/cell death probe. Stein LS, PD Quintel, S Krajewski,JS Rosenberg, SK Singh. Cancer Res 72:237 (2012). Flow (Cell Surface):Jurkat (Figs 1-4). IF: Mouse primary neuronal cultures (Figs 5-6).
[17] Diurnal photoreceptor outer segment shedding: contributions of the RPE. Finnemann SC, L Ruggiero, MP Connor. Invest Opthalmol Vis Sci 53:4327 (2012). Live Imaging: mouse retina. pSIVA was used quantify the surface exposure of phosphotidylserine on the distal rod photore- ceptor outer segments.
[18] Flavopiridol synergizes with sorafenib to induce cytotoxicity and potentiate antitumorigenic activity in EGFR/HER-2 and mutant RAS/RAF breast cancer model systems. Nagaria TS, JL Williams, C Leduc, JA Squire, PA Greer, W Sangrar. Neoplasia 15:939-951 (2013). Flow cytometry (Cell surface): MDA-MB-231 (Fig 4A) and MDA-MB-468 (Fig 4B) adenocarcinoma cells.???????联科生物代理截止时间:2017年6月30日
|