Anti-Human CD105, APC (Clone: 00244) 检测试剂
¥1,544.00 – ¥3,264.00
因产品会迭代升级,具体实验步骤请按纸质版说明书操作
- 分子靶点:RNG, endoglin, CD105
- 种属:人 (Human)
- 标记:APC
- 亚型:Mouse IgG1, κ
- 克隆号:00244
在售SKU, F1110503, 70-F1110503-25, 70-F1110503-100
| 商品名 |
Anti-Human CD105, APC (Clone: 00244) 检测试剂 |
|---|---|
| 靶点 | |
| 标记 |
APC |
| 仪器 |
适用633nm激光器的流式细胞仪 |
| 亚型 |
Mouse IgG1, κ |
| 克隆号 |
00244 |
| 推荐应用 |
流式检测 |
| 用量 |
5 μL/Test |
| 纯化 |
亲和层析 |
| 储存液 |
含 0.2% BSA 和 0.2% proclin 950 的磷酸盐缓冲液(pH7.2) |
| 保存条件 |
2 - 8℃避光,切勿冻存 |
结果示例
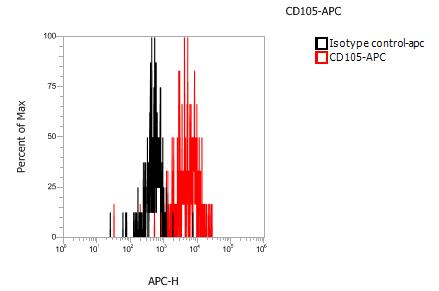
图 - 人白血病细胞(TF-1)染色,Mouse IgG1, κ Isotype control, APC和Anti-Human CD105, APC的染色结果。
分子信息
ENG 分子靶点信息概述
- 分子名:ENG, endoglin
- 基因家族:CD molecules
- 别名:END; HHT1; CD105
- 曾用名:ORW1; ORW
- 全称:Osler-Rendu-Weber syndrome 1
ENG 分子靶点综述
内皮糖蛋白(Endoglin),又称为CD105,是位于细胞膜表面的I型跨膜糖蛋白,是TGF-β受体复合物之一。它参与调控与TGF-β1、TGF-β3、Activin-A、BMP-2和BMP-7结合的应答。Endoglin被推测参与影响细胞形态和迁移的细胞骨架构成。它在心血管系统发育和血管重塑中发挥作用。在心脏发育过程中,Endoglin的表达受到调控。缺失Endoglin基因的实验小鼠由于心血管异常而死亡。在人类中,Endoglin可能参与常染色体显性疾病,为人熟知的是1型遗传性出血性毛细血管扩张症(HHT)。它会导致频繁的鼻出血、皮肤和粘膜毛细管扩张,在不同的器官(如大脑、肺和肝脏)中引起动静脉畸形。
人 Human ENG 分子靶点信息
- 分子名:ENG, endoglin
- 别称:
- CD105
- CD105 antigen
- END
- FLJ41744
- HHT1
- ORW
- ORW1
- 基因序列:NCBI_Gene: 2022
- 蛋白序列:UniProtKB: P17813
人 Human ENG靶点分子功能(预测)
Enables several functions, including galactose binding activity; protein homodimerization activity; and transforming growth factor beta receptor binding activity. Contributes to BMP binding activity and transforming growth factor beta binding activity. Involved in several processes, including central nervous system vasculogenesis; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II; and regulation of transmembrane receptor protein serine/threonine kinase signaling pathway. Located in external side of plasma membrane; extracellular space; and nuclear body. Part of receptor complex. Implicated in arteriovenous malformation; arteriovenous malformations of the brain; breast cancer; hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia; and intracranial aneurysm. Biomarker of several diseases, including artery disease (multiple); clear cell renal cell carcinoma; diabetic retinopathy; hematologic cancer (multiple); and secondary hyperparathyroidism.